25/11/2021
Learn How To Test For Diabetes
Table of Contents
Diabetes symptoms – what does it feel like to have high blood sugar? What are the risk factors and who should take the test? Read on to find out more about testing for diabetes, what it involves and and how to do it from home.
Diabetes target blood sugar levels are important to understand for patients who have active Diabetes Mellitus or are testing to diagnose diabetes. This guide helps you to understand why, when and how and when to test your blood sugar.
Diabetes symptoms – what does it feel like to have high blood sugar?
Often higher blood sugar levels will have very few symptoms or no symptoms at all. People who have pre-diabetes (impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose) have higher than normal average blood sugar levels and may do so for many months or years before they are aware. Your body is struggling to keep your blood sugar levels in the normal range. When this progresses to diabetes the blood sugar levels are higher leading to symptoms of
- Fatigue and feeling unwell
- Frequent urination
- Hungry
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
Risk factors for high blood sugar
The risk factors for having abnormal blood sugar levels are the same as the risks for developing diabetes:
- Overweight and obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle (being inactive)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Poor diet
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Family history of Type 2 diabetes
People with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), gestational diabetes, Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander background, backgrounds from Pacific Islands, Asia and Indian sub-continent.
Who should have a diabetes test?
If you have developed any symptoms of diabetes, are you are concerned about your risk factors, you should see your general practitioner to discuss the risk of diabetes and whether you need to be tested. You doctor will undertake a risk assessment using the Australian Type 2 Diabetes Risk Assessment Tool (AUSDRISK).
How to test for diabetes
Following the risk assessment your doctor will consider undertaking a number of tests. You may have a random blood glucose test in the doctors office. This involves a fingerprick blood test using a glucometer to test your current blood sugar level. The doctor may also test your urine using a urine dipstick test. This will test for sugar and ketones in your urine.
Diabetes blood test
The definitive way to test for diabetes involves a blood glucose test. A blood sample is taken at a pathology collection centre and sent to the laboratory for analysis. There are various types of tests but most commonly you will be asked to have a fasting blood glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test. You will be asked to fast overnight and then at the pathology collection centre have a sugary drink that is provided for you. You blood test is then taken 2hrs later.
How much does a diabetes test cost?
In Australia, with a valid Medicare card your blood glucose test as ordered by the doctor will be bulk billed meaning there are no out of pocket expenses for you. Double check this with your doctor and the pathology laboratory.
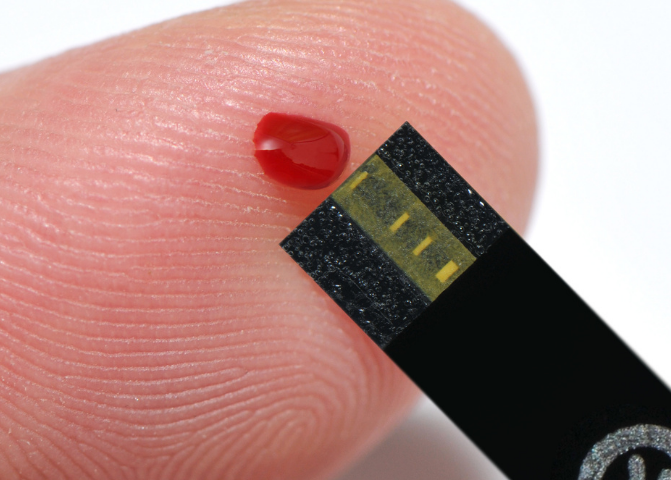
Touch the blood testing strip to the drop of blood.
How to test your blood sugar regularly
If you have diabetes your doctor and diabetes educator will ask you to test your blood sugar levels regularly and keep a record of the results. This will involve the use of a blood glucose meter called a glucometer. There are several brands on the market that are very accurate including Accu-Check. May sure that you spend time with your diabetes educator understanding how to use the blood glucose meter. You will follow some simple steps:
- Wash your hands with soap and water and dry well.
- Insert a blood glucose testing strip into the glucometer.
- Using the lancet device to prick the side of your fingertip to extract a drop of blood.
- Touch the test strip to the drop of blood
- The blood glucose meter will display the blood sugar level on the screen
- Record this reading in your blood glucose diary with the date and time and any notes (eg. “fasting” or “2hrs after breakfast”).
There are some great apps that help you keep track of your blood glucose readings and share these easily with your doctor and diabetes educator.
Diabetes target blood sugar levels
Blood sugar control is only one of the important factors in good diabetes management. Have a read of our Quick Guide To Diabetes Treatment.
Recommended reading
Search for a specific topic or filter by categories to find information on what you need to know on the full Medmate Journal

What Are Antihistamines and How Do They Work?
If you experience sneezing fits in spring, itchy skin after contact with something new, or watery eyes around pets, you may have been told to take an antihistamine. But what…

