UTIs – A Complete Guide Causes and Treatment
Table of Contents
What are UTIs (urinary tract infections)? Understand the most common symptoms for the illness and what you can do to treat it including the use of antibiotics and their appropriate dosages.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a very common problem in all ages. In particular, they are very common in sexually active women and less common in men and children.
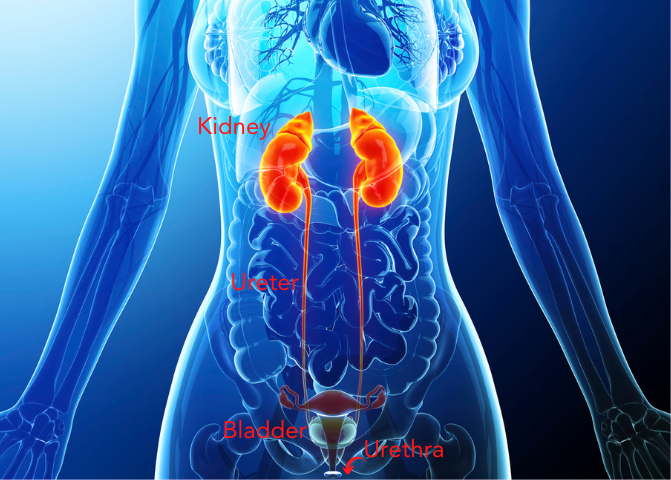
The urinary tract is the collection of body parts that allow the body to excrete water and waste in the form of urine. Most people have two kidneys and have a pipe that connects each kidney to the bladder. The bladder collects urine and signals an urge to urinate. Urine leaves the bladder through another tube called the urethra. Urine flows one way from the kidneys all the way down through the urethra to the external environment. Infections tend to occur in the bladder (cystitis) but can spread to any part of the urinary tract including the kidneys and blood system (sepsis) which are very serious, potential life threatening conditions.
What is a UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)?
UTIs are caused by germs, most commonly types of bacteria that infect a part of the urinary tract. Doctors define the type of urinary tract infection depending on the level of the system involved.
Cystitis – infection of the bladder. This is the most commonly experienced UTI.
Urethritis – infection of the urethra, the pipe leading to the external environment from the bladder.
Pyelonephritis – infection of the kidneys themselves, usually from infection spreading upwards from the bladder.
What are the causes of a UTI?
The urinary tract system is normally a sterile environment – no germs. Infection occurs when bacteria enter the sterile system and cause an infection.
The bacteria involved generally originate from the bowel and reach the bladder by the urethra. Ascending infection accounts for over 90% of UTIs.
Most UTIs are caused by bacteria called Escherichia coli (70 to 95% of cases) and Staphylococcus saprophyticus (5 to 10% of cases).
Risk factors for UTI include:
- Being female
- Sexual intercourse – mechanical abrasion seems to aggravate the area
- Diabetes
- Diaphragm use
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
- Urinary tract abnormalities
- Bladder polyps, cancers
- Diverticulitis
Symptoms – What are they?
The most common symptoms of a UTI are:
- Urinary frequency : passing urine a lot more often than normal
- Pain on urination – discomfort or burning sensation on passing urine
- Lower abdominal discomfort
- Lower back pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Smelly, cloudy or blood tinged urine
In children symptoms can be more general:
- Fever
- Irritability
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting or diahorrea
- Lethargy
The symptoms of a UTI can commonly mimick other serious conditions such as appendicitis or gallbladder infection. It’s important to seek medical attention to discuss your symptoms with a doctor.
Treatment for UTI
Your doctor may consider immediate medical therapy for a UTI. Talk to a Medmate doctor online today.
Join the Medmate Community!
Receive free expert health advice from Australian doctors and health advisors. Join the Medmate community now - just what the doctor ordered.
Health Information I Medication Education & Tips I Patient Stories & Videos.