01/06/2024
Understand Chest Infections: Symptoms and Causes
A chest infection refers to various respiratory illnesses affecting the lungs or airways, including bronchitis and pneumonia. These conditions can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi.
What is a Chest Infection?
A chest infection, medically known as lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), encompasses a range of illnesses affecting the lungs or airways. It’s a prevalent condition worldwide, including in Australia, and can vary in severity from mild to life-threatening. Understanding the nuances of chest infections is crucial for effective prevention, management, and treatment.
Types of Chest Infections
Chest infections can manifest in various forms, with the most common types including:
Bronchitis
This condition involves inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs. Acute bronchitis is often caused by viral infections, while chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) commonly associated with smoking.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and its severity can range from mild to severe, with some cases requiring hospitalization.
Bronchiolitis
This condition primarily affects infants and young children, causing inflammation and congestion in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. It is usually caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and can lead to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is characterized by inflammation of the pleura, the thin membranes that line the chest wall and cover the lungs. It often causes sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing and can be a complication of respiratory infections like pneumonia or tuberculosis.
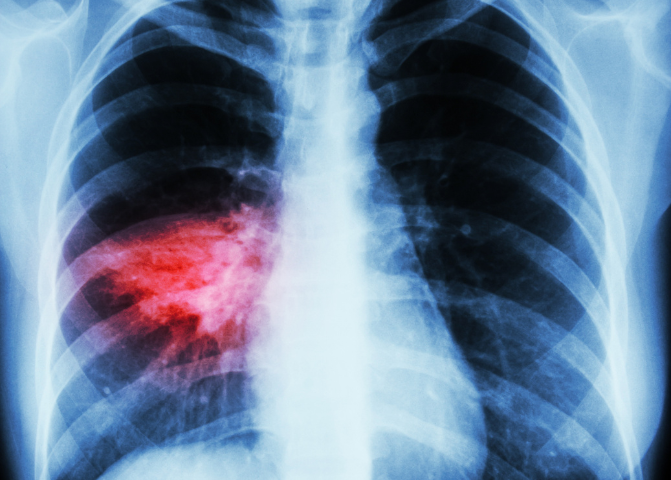
Severe chest infections, like pneumonia, can be life threatening. Seek medical advice.
Causes of Chest Infections
Chest infections can be caused by various infectious agents, including:
Viruses
Common viral pathogens responsible for chest infections include influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, and adenovirus. Viral chest infections are often highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Bacteria
Bacterial infections, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, can also cause chest infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis. Bacterial chest infections may require antibiotic treatment, especially in cases of severe or prolonged illness.
Fungi
Fungal chest infections are less common but can occur in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying lung conditions. Aspergillus species are among the most common fungi responsible for causing chest infections, particularly in individuals with asthma or cystic fibrosis.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental pollutants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards can increase the risk of developing chest infections. Smoking, in particular, is a significant risk factor for respiratory conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia.
Can Covid-19 Cause a Chest Infection?
Yes, COVID-19 can cause a chest infection. COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, primarily affects the respiratory system. In some cases, the infection can lead to pneumonia, a type of chest infection. Symptoms of a chest infection from COVID-19 may include:
– Cough
– Fever
– Shortness of breath
– Chest pain or discomfort
– Fatigue
Severe cases can result in significant lung inflammation and damage, potentially leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which requires medical attention. It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms of a chest infection, especially if they worsen or do not improve.
Common Symptoms of Chest Infections
1. Cough: Often persistent and can produce mucus that may be green, yellow, or blood-streaked.
2. Fever: A high temperature is common, sometimes accompanied by chills.
3. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless.
4. Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
5. Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or exhausted.
6. Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing.
7. Headache: Often due to the strain of coughing or from fever.
8. Muscle Aches: Generalized body aches and muscle pain.
9. Sweating and Shivering: Alternating between feeling hot and cold.
10. Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
These symptoms can vary in severity and may be more pronounced in individuals with underlying health conditions or weakened immune systems. If you suspect a chest infection, it is advisable to seek medical attention, especially if symptoms are severe or persistent.
Risk factors for developing chest infections
1. Age: Very young children and older adults are more susceptible.
2. Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, and immunosuppressive medications can lower immunity.
3. Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other lung diseases increase risk.
4. Smoking: Damages the lungs and weakens the respiratory system.
5. Recent Surgery or Hospitalization: Especially involving the chest or abdomen, increasing vulnerability to infections.
6. Pre-existing Conditions: Diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease can increase susceptibility.
7. Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, allergens, and crowded living conditions can elevate risk.
8. Viral Infections: Previous viral infections, like the flu, can lead to secondary bacterial infections in the chest.
9. Alcohol Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair the immune system.
10. Poor Nutrition: Malnutrition can weaken the body’s defenses against infections.
11. Chronic Sinusitis: Persistent sinus infections can spread to the chest.
12. Obesity: Can restrict lung function and increase the risk of infections.
Maintaining good hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and managing existing health conditions can help reduce the risk of developing chest infections.
Preventative Measures for Chest Infections
Preventative measures for chest infections involve a combination of lifestyle practices and medical interventions aimed at maintaining respiratory health and strengthening the immune system. Key strategies include practicing good hygiene, such as regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, to reduce the spread of infectious agents. Vaccinations, particularly the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine, are crucial in preventing respiratory infections that can lead to chest complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can enhance overall immune function. Managing chronic conditions like asthma, diabetes, and heart disease effectively through regular medical check-ups and adherence to treatment plans is essential. Additionally, ensuring good indoor air quality by reducing exposure to pollutants and allergens can help protect respiratory health. Finally, staying hydrated and practicing proper cough etiquette, such as covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow, can minimize the risk of spreading infections.
When to see a Doctor About a Chest Infection
It’s important to see a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms or conditions related to a chest infection:
1. Severe or Persistent Symptoms: If your cough, fever, or chest pain persists for more than a few days or worsens over time.
2. Difficulty Breathing: If you experience shortness of breath, wheezing, or a feeling of not getting enough air.
3. High Fever: A fever of 37.5C or higher that does not improve with over-the-counter medications.
4. Coughing up Blood: If you notice blood in your mucus or phlegm.
5. Chest Pain: Severe chest pain that worsens with deep breaths, coughing, or movement.
6. Confusion or Disorientation: Particularly in older adults, this can be a sign of a severe infection.
7. Underlying Health Conditions: If you have chronic illnesses such as asthma, COPD, diabetes, or heart disease that could be exacerbated by a chest infection.
8. Weak Immune System: If you have a compromised immune system due to conditions like HIV, cancer treatments, or immunosuppressive medications.
9. Symptoms in Young Children or Elderly: Both age groups are more vulnerable to complications from chest infections.
10. No Improvement: If there is no improvement after a few days of home treatment, or if symptoms return after getting better.
Seeking medical attention in these situations can help ensure timely and appropriate treatment, reducing the risk of complications and promoting a faster recovery. Medmate doctors are online 24/7 for immediate advice. Book a consult.
Recovery and Management of Chest Infections
Recovery and management of chest infections require a combination of medical treatment and self-care strategies to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Following a doctor’s prescribed treatment plan, which may include antibiotics for bacterial infections or antiviral medications for viral infections, is crucial. Resting adequately allows the body to focus energy on fighting the infection. Staying hydrated helps to thin mucus, making it easier to expel, while using a humidifier can soothe irritated airways. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and fever reducers, can help manage symptoms like fever, headache, and muscle aches. Practicing good hygiene, including frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with others, prevents the spread of infection. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports the immune system. Avoiding smoking and exposure to pollutants is important to prevent further irritation of the respiratory tract. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider ensure the infection is fully resolved and address any complications that may arise during recovery.
Recommended reading
Search for a specific topic or filter by categories to find information on what you need to know on the full Medmate Journal

What Are Antihistamines and How Do They Work?
If you experience sneezing fits in spring, itchy skin after contact with something new, or watery eyes around pets, you may have been told to take an antihistamine. But what…
